How to Identify Diode Symbols and PCB Layouts
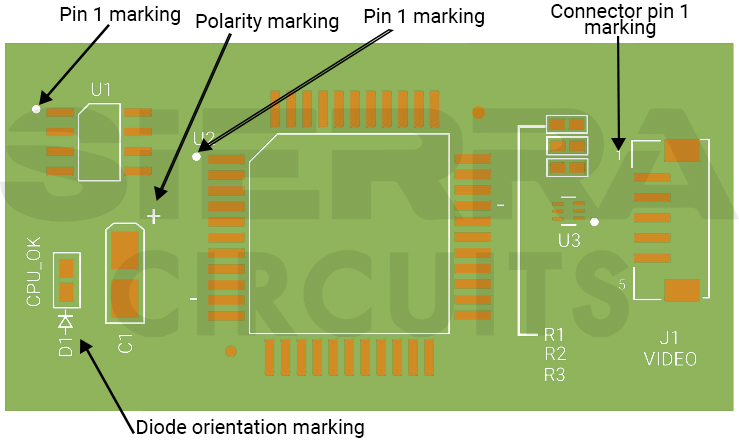
Diodes are among the most common electronic components found on printed circuit boards (PCBs), including mobile phone motherboards. Correctly identifying diode symbols and their physical layout is essential for troubleshooting power, charging, signal, and protection circuits.
What Is a Diode?
A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor component that allows electric current to flow in only one direction. The two terminals are known as the Anode and Cathode.
Diodes are widely used for:
- Voltage and current rectification
- Voltage stabilization and regulation
- Signal protection and isolation
- AC to DC conversion
Identifying Diode Symbols in Circuit Diagrams

In schematic diagrams, a diode is represented by a triangle pointing toward a vertical line. The triangle represents the anode, while the vertical line represents the cathode.
On PCB silkscreens and circuit diagrams, diodes are often labeled with the letter “D” or “V”, followed by a number (for example: D101, V203). These markings help technicians locate and identify the component during repair.
Zener Diode Symbol and Function
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction once a specific voltage threshold—called the Zener voltage—is reached.
Zener diodes are commonly used for voltage regulation and overvoltage protection in mobile phone circuits.
Identifying Diodes on a Printed Circuit Board
On a PCB, diodes are usually small, rectangular, or cylindrical components. The cathode side is often marked with:
- A white or black stripe
- A printed line on the PCB silkscreen
- A square solder pad (in some designs)
Correct orientation is critical. Installing a diode backward can cause circuit failure or short circuits.
Light Emitting Diode (LED)

A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a diode that produces visible light when forward biased. LEDs are commonly used as indicators, backlights, flash lights, and notification lights in mobile phones.
How LEDs Work
When current flows through an LED, electrons recombine with holes inside the semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons. This phenomenon is known as electroluminescence.
The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material and its energy band gap.
Photodiode (Photo Cell)

A photodiode is a light-sensitive diode capable of converting light energy into electrical current or voltage. Unlike LEDs, photodiodes work in reverse—they receive light instead of emitting it.
Uses of Photodiodes in Mobile Phones
- Ambient light sensors
- Proximity sensors
- Camera flash detection
- Automatic brightness control
Photodiodes are also widely used in solar panels, optical communication systems, and light detection applications.
Summary
Understanding diode symbols and PCB layouts is a fundamental skill in mobile phone hardware repair. Whether identifying standard rectifier diodes, Zener diodes, LEDs, or photodiodes, recognizing their symbols, orientation, and function allows technicians to diagnose power, charging, and signal-related faults accurately.
Always verify diode orientation and function using a multimeter in diode test mode before replacement or circuit modification.
إرسال تعليق